When you hear the term "SPF," you might automatically think of sunscreen and beach days. But what does the SPF number mean, and why is it so important for our skin health? SPF, or Sun Protection Factor, is a metric used to determine how well a sunscreen can protect your skin from harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays. Understanding SPF is crucial because it directly impacts how we protect ourselves from sunburn, premature aging, and even skin cancer. In this article, we'll delve into the science behind SPF, how it's measured, and why it's a vital consideration in your daily skincare routine.
In recent years, awareness about the damaging effects of UV radiation has significantly increased. Consequently, SPF has become a buzzword in the beauty and skincare industries. However, despite its popularity, many people still have questions about SPF, how it works, and what the numbers really mean. Is a higher SPF always better? How often should you reapply sunscreen? These are just a few of the common questions that arise when discussing SPF. Our goal is to provide clear, evidence-based answers to these questions, empowering you to make informed decisions about sun protection.
Whether you're planning a day at the beach or just running errands, understanding SPF can help you better protect your skin. This article will explore the different types of sunscreens available, the meaning behind SPF numbers, and how to choose the right product for your skin type and lifestyle. By the end of this guide, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of what SPF is, how it functions, and why it's an essential component of your skincare regimen. Let’s dive in and uncover the facts about SPF, ensuring you stay sun-safe all year round.
Read also:Benefits And Uses Of Natural Body Oil For Skin Health
Table of Contents
- What is SPF?
- How is SPF Measured?
- What Do the SPF Numbers Mean?
- Is a Higher SPF Better?
- Types of Sunscreens
- Choosing the Right SPF
- SPF and Skin Types
- SPF and Sunscreen Application
- How Often Should You Reapply Sunscreen?
- SPF in Daily Skincare
- Common Misconceptions About SPF
- Benefits of Using SPF
- SPF and Environmental Impact
- SPF and Skin Health
- FAQs
- Conclusion
What is SPF?
SPF stands for Sun Protection Factor. It is a measure of how well a sunscreen will protect skin from UVB rays, the kind of radiation that causes sunburn and contributes to skin cancer. The SPF number is a relative measure of how long a sunscreen will protect you from ultraviolet (UV) rays.
The concept of SPF was first introduced in 1962 by Franz Greiter, a Swiss chemist who was inspired by his own sunburn experience. He developed a cream called Gletscher Crème (Glacier Cream) and assigned it an SPF rating. The idea was to create a standard by which sunscreens could be measured for their effectiveness.
Today, SPF is a crucial element in sun protection products, helping consumers choose the right level of protection for their needs. It's important to note that SPF only measures UVB protection, while UVA protection is indicated separately. Both UVA and UVB rays can harm the skin, so comprehensive protection is essential.
How is SPF Measured?
The SPF rating is determined through a series of clinical tests involving human subjects. In a laboratory setting, a small area of a person's skin is exposed to a UV lamp until it starts to redden, which is known as the minimal erythemal dose (MED). This test is done with and without sunscreen to determine the ratio of UV exposure that causes sunburn.
The SPF value is calculated using the formula:
- SPF = (MED with sunscreen) / (MED without sunscreen)
For example, if it takes 15 times longer to redden the skin with sunscreen than without, the SPF rating would be 15. This means that theoretically, you could stay in the sun 15 times longer without getting sunburned.
Read also:Understanding The Dynamics Of Zodiac Sun And Moon Signs
It's important to remember that SPF testing conditions are controlled and may not reflect real-world usage, where factors like sweating, swimming, and towel-drying can reduce sunscreen effectiveness. This is why reapplication is crucial.
What Do the SPF Numbers Mean?
The SPF number on a sunscreen label indicates the level of protection it provides against UVB rays. The higher the SPF, the more protection you get, but it doesn't mean you can stay in the sun indefinitely. Here's a general breakdown of SPF levels:
- SPF 15: Blocks about 93% of UVB rays.
- SPF 30: Blocks around 97% of UVB rays.
- SPF 50: Blocks approximately 98% of UVB rays.
- SPF 100: Blocks roughly 99% of UVB rays.
While higher SPF numbers do offer more protection, no sunscreen can block 100% of UVB rays. Additionally, higher SPF sunscreens can give a false sense of security, leading people to stay in the sun longer than they should.
It's also worth noting that the difference in protection between SPF 30 and SPF 50 is only about 1%. Therefore, it's more important to apply sunscreen generously and reapply regularly rather than relying solely on a higher SPF number.
Is a Higher SPF Better?
While it might seem logical to assume that a higher SPF offers significantly better protection, the reality is more nuanced. As mentioned earlier, the increase in UVB protection is marginal beyond SPF 30 or 50. Here are some points to consider:
- Marginal Gains: The difference between SPF 30 and SPF 50 in terms of UVB protection is just 1%.
- False Sense of Security: Higher SPF can lead to longer sun exposure, increasing the risk of UVA damage.
- Cost: Higher SPF sunscreens often cost more, without providing significantly better protection.
Ultimately, the best sunscreen is one that you will use consistently. It's vital to apply it correctly and reapply every two hours, or more frequently if you're swimming or sweating.
Types of Sunscreens
Sunscreens are generally categorized into two types: chemical and physical. Each type has its own unique characteristics and benefits.
Chemical Sunscreens
Chemical sunscreens absorb UV radiation and convert it into heat, which is then released from the skin. These sunscreens contain active ingredients like oxybenzone, avobenzone, octisalate, and octocrylene.
- Pros: Lightweight and less visible on the skin, often more water-resistant.
- Cons: Can cause irritation for sensitive skin, requires time to absorb before sun exposure.
Physical Sunscreens
Physical sunscreens, also known as mineral sunscreens, use active mineral ingredients such as titanium dioxide or zinc oxide. These ingredients sit on top of the skin, reflecting UV rays.
- Pros: Less likely to cause irritation, provides immediate protection.
- Cons: Can be thicker and more visible on the skin, may not be as water-resistant.
Choosing between chemical and physical sunscreens depends on personal preference, skin type, and specific needs. Some sunscreens combine both types for broad-spectrum protection.
Choosing the Right SPF
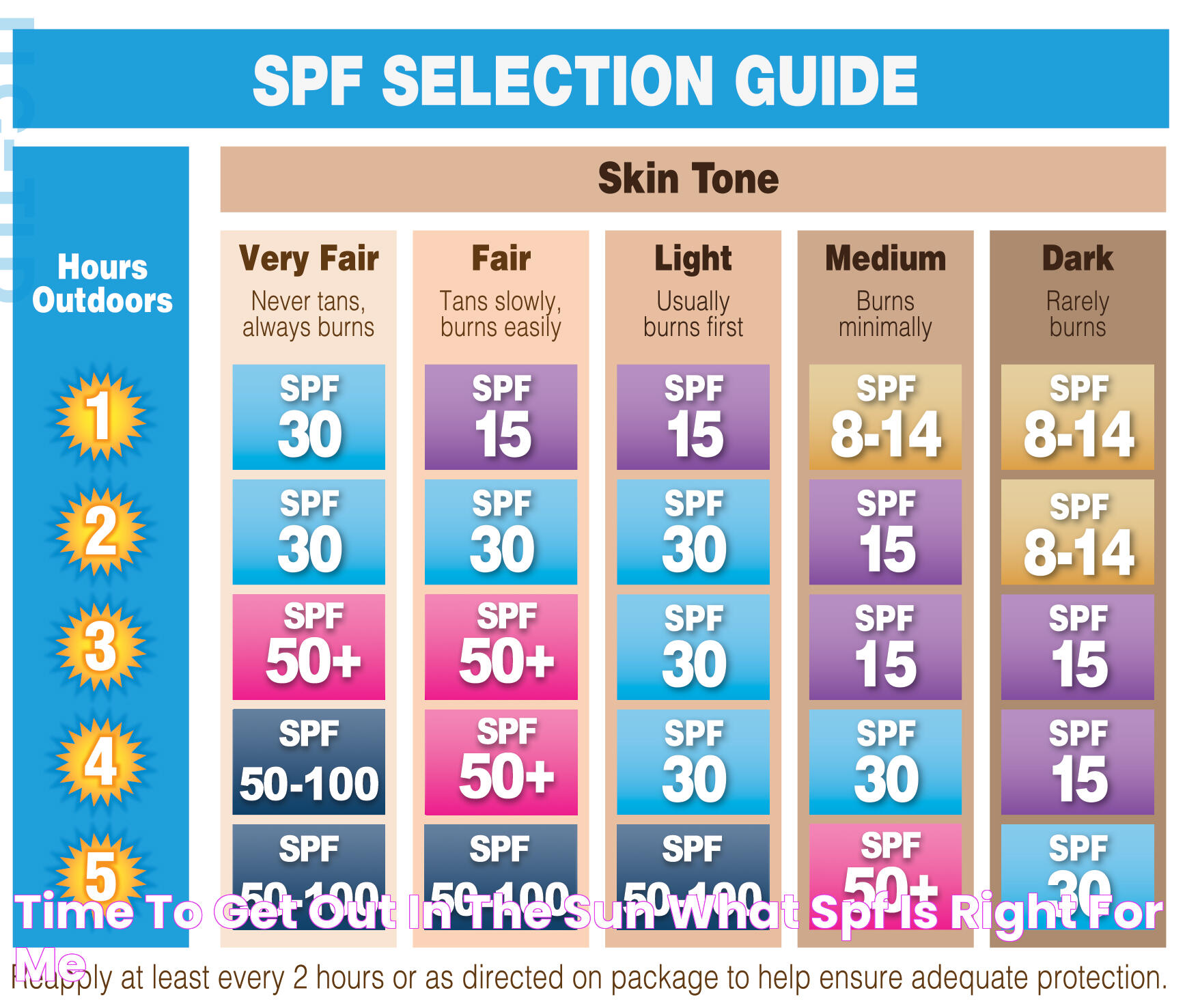
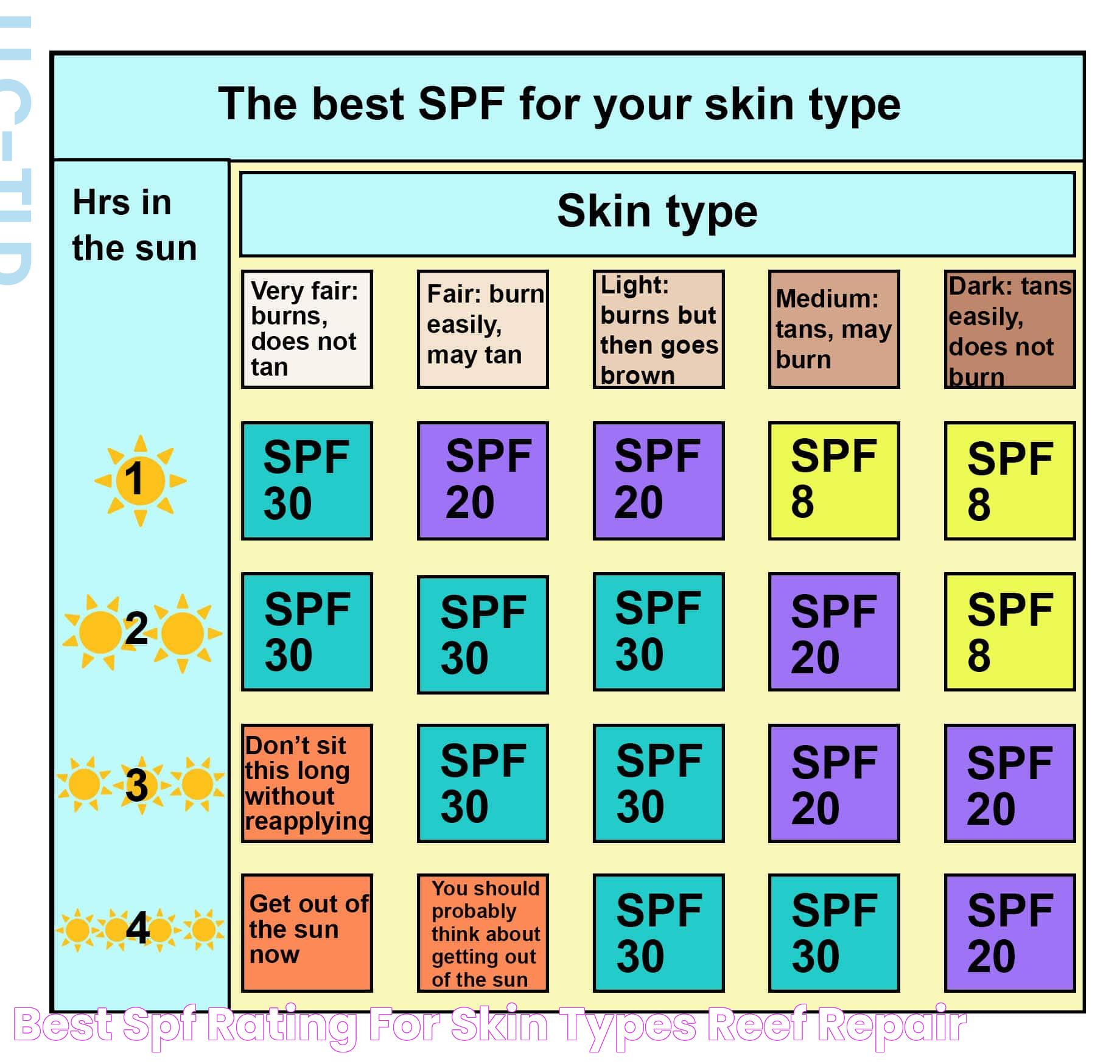
Selecting the appropriate SPF level involves considering your skin type, the duration of sun exposure, and environmental factors. Here are some guidelines:
- Skin Type: Fair-skinned individuals may require a higher SPF due to increased susceptibility to sunburn.
- Activity Level: If you're engaging in water sports or sweating, opt for water-resistant formulas.
- Time of Day: The sun's rays are strongest between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., so higher SPF is advisable during these hours.
For most people, SPF 30 is sufficient for daily use, while SPF 50 or higher may be necessary for extended outdoor activities. Remember, reapplication is key to maintaining protection.
SPF and Skin Types
Different skin types have varying levels of sensitivity to the sun, affecting the choice of SPF. Here's how to tailor SPF to your skin type:
- Fair Skin: Fair-skinned individuals are more prone to sunburn and should use a higher SPF, typically SPF 30 or higher.
- Medium Skin: Those with medium skin tones can generally use SPF 15 to 30 for everyday protection.
- Dark Skin: While melanin offers some natural protection, dark-skinned individuals should still use SPF 15 or higher to prevent UV damage.
Regardless of skin type, everyone should use sunscreen to protect against both UVB and UVA rays. Broad-spectrum sunscreens offer comprehensive protection.
SPF and Sunscreen Application
Proper application of sunscreen is crucial to ensuring effective protection. Here are some tips for applying sunscreen correctly:
- Amount: Use approximately one ounce (a shot glass full) to cover the entire body.
- Timing: Apply sunscreen 15-30 minutes before going outside to allow it to absorb into the skin.
- Method: Ensure even coverage, paying attention to often-missed areas like ears, neck, and tops of feet.
Reapplication is necessary, especially after swimming, sweating, or towel-drying. Aim to reapply every two hours for continuous protection.
How Often Should You Reapply Sunscreen?
Sunscreen's effectiveness diminishes over time, necessitating regular reapplication. As a general rule, reapply sunscreen every two hours, or more frequently if you're swimming, sweating, or towel-drying.
- Water Activities: Use water-resistant sunscreens and reapply immediately after swimming or heavy perspiration.
- Extended Outdoor Time: Reapply more frequently if spending a long time outdoors, especially during peak sun hours.
Regular reapplication ensures that you maintain adequate protection throughout the day, reducing the risk of sunburn and long-term skin damage.
SPF in Daily Skincare
Incorporating SPF into your daily skincare routine is a proactive way to protect your skin. Many moisturizers and makeup products now include SPF for added convenience. Here are some tips for integrating SPF:
- Moisturizers: Choose a daily moisturizer with SPF 15 or higher for everyday protection.
- Makeup: Consider foundations or BB creams with SPF for an added layer of defense.
- Layering: Apply a dedicated sunscreen underneath makeup for optimal protection.
By making SPF a part of your daily routine, you're taking an important step toward preserving your skin's health and appearance.
Common Misconceptions About SPF
Despite widespread awareness of SPF, several misconceptions persist. Let's address some of the most common myths:
- Myth 1: You only need sunscreen on sunny days.
- Fact: UV rays can penetrate clouds, so sunscreen is necessary even on overcast days.
- Myth 2: People with darker skin don't need sunscreen.
- Fact: While melanin offers some protection, everyone is susceptible to UV damage and should use sunscreen.
- Myth 3: One application of sunscreen lasts all day.
- Fact: Sunscreen needs to be reapplied every two hours for continuous protection.
Understanding these misconceptions can help you make better-informed decisions regarding sun protection and skincare.
Benefits of Using SPF
Regular use of SPF offers numerous benefits, contributing to both short-term and long-term skin health. Here are some key advantages:
- Prevents Sunburn: SPF protects against painful sunburn, which can cause skin peeling and discomfort.
- Reduces Skin Cancer Risk: Sunscreen use lowers the risk of developing skin cancer, including melanoma.
- Slows Aging: Regular SPF use helps prevent premature aging, such as wrinkles and sunspots.
By incorporating SPF into your daily routine, you're safeguarding your skin from the harmful effects of UV radiation.
SPF and Environmental Impact
While SPF is essential for skin protection, some sunscreen ingredients can harm the environment, particularly marine life. Here's what you need to know:
- Coral Reefs: Certain chemicals in sunscreens, such as oxybenzone, can damage coral reefs.
- Eco-Friendly Options: Look for "reef-safe" sunscreens that use minerals like zinc oxide and titanium dioxide.
Choosing environmentally friendly sunscreens helps protect not only your skin but also the planet.
SPF and Skin Health
SPF plays a vital role in maintaining overall skin health. By protecting against UV damage, SPF helps preserve your skin's integrity and appearance. Here are some skin health benefits:
- Prevents Sun Damage: SPF shields skin from harmful UV rays, reducing the risk of sunburn and long-term damage.
- Supports Healing: Regular use of SPF allows the skin to heal and regenerate without interference from UV exposure.
By prioritizing SPF, you're investing in the long-term health and beauty of your skin.
FAQs
- What does the SPF number mean?
- Is SPF 30 enough for daily use?
- Can I use sunscreen on cloudy days?
- What’s the difference between UVA and UVB protection?
- How often should I reapply sunscreen?
- Are there sunscreens safe for the environment?
The SPF number indicates the level of protection a sunscreen provides against UVB rays. Higher numbers offer more protection, but no sunscreen blocks 100% of UVB rays.
Yes, SPF 30 is generally sufficient for daily use. It blocks about 97% of UVB rays, providing adequate protection for most people.
Absolutely. UV rays can penetrate clouds, so it's important to use sunscreen even on overcast days.
UVB rays cause sunburn, while UVA rays penetrate deeper into the skin, causing premature aging. Broad-spectrum sunscreens protect against both.
Reapply sunscreen every two hours, or more frequently if you're swimming, sweating, or towel-drying.
Yes, look for "reef-safe" sunscreens that use mineral ingredients like zinc oxide or titanium dioxide, which are less harmful to marine life.
Conclusion
Understanding what does the SPF number mean is essential for making informed decisions about sun protection. SPF is a crucial factor in safeguarding your skin from harmful UV radiation, reducing the risk of sunburn, premature aging, and skin cancer. Whether you're enjoying a day at the beach or running daily errands, using the right SPF can make a significant difference in your skin's health and appearance. Remember to choose the appropriate SPF for your skin type and activities, apply it correctly, and reapply as needed. By incorporating SPF into your daily routine, you're taking a proactive step toward maintaining healthy, beautiful skin for years to come.
For further reading on sun protection and skincare, visit the Skin Cancer Foundation for expert advice and resources.