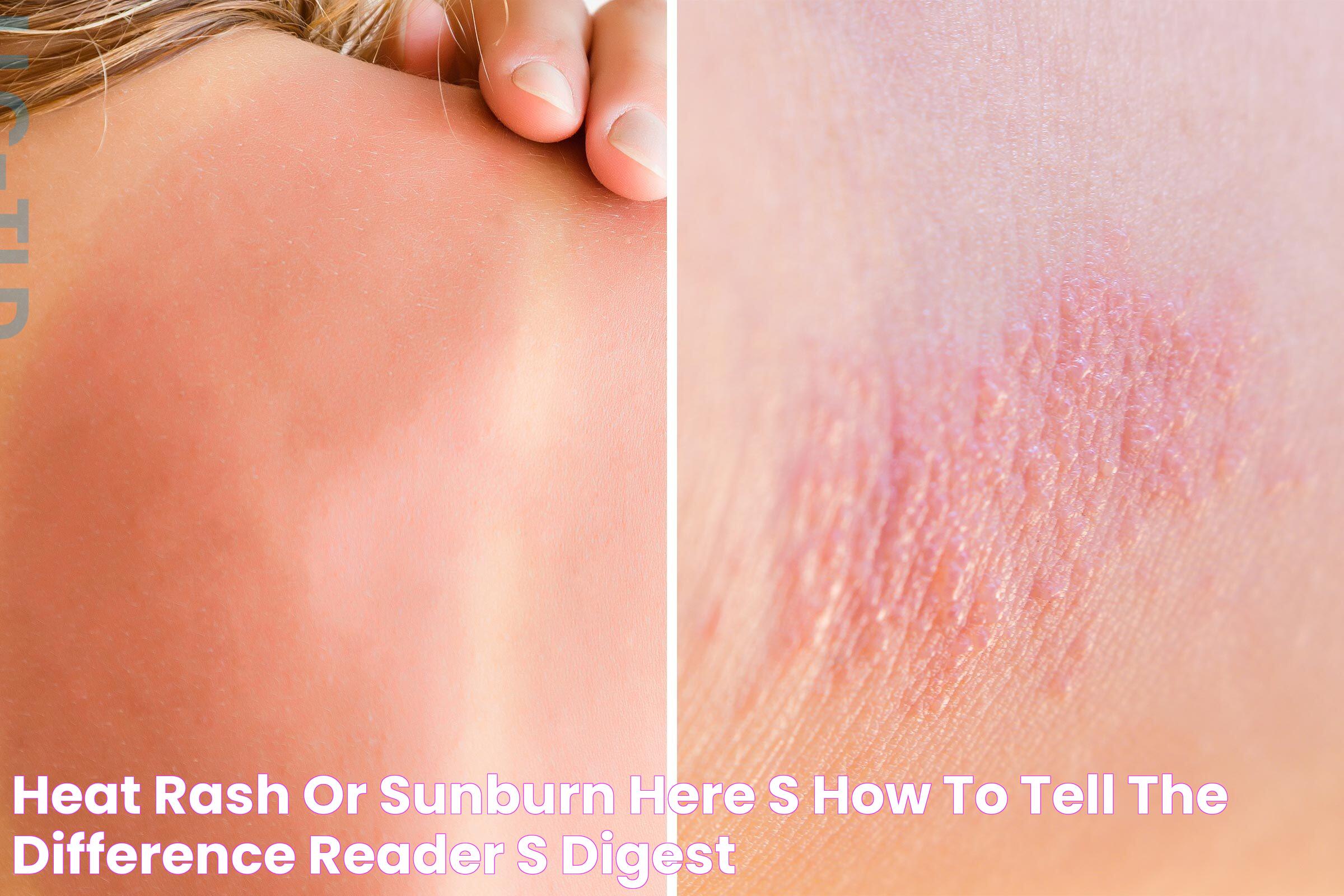
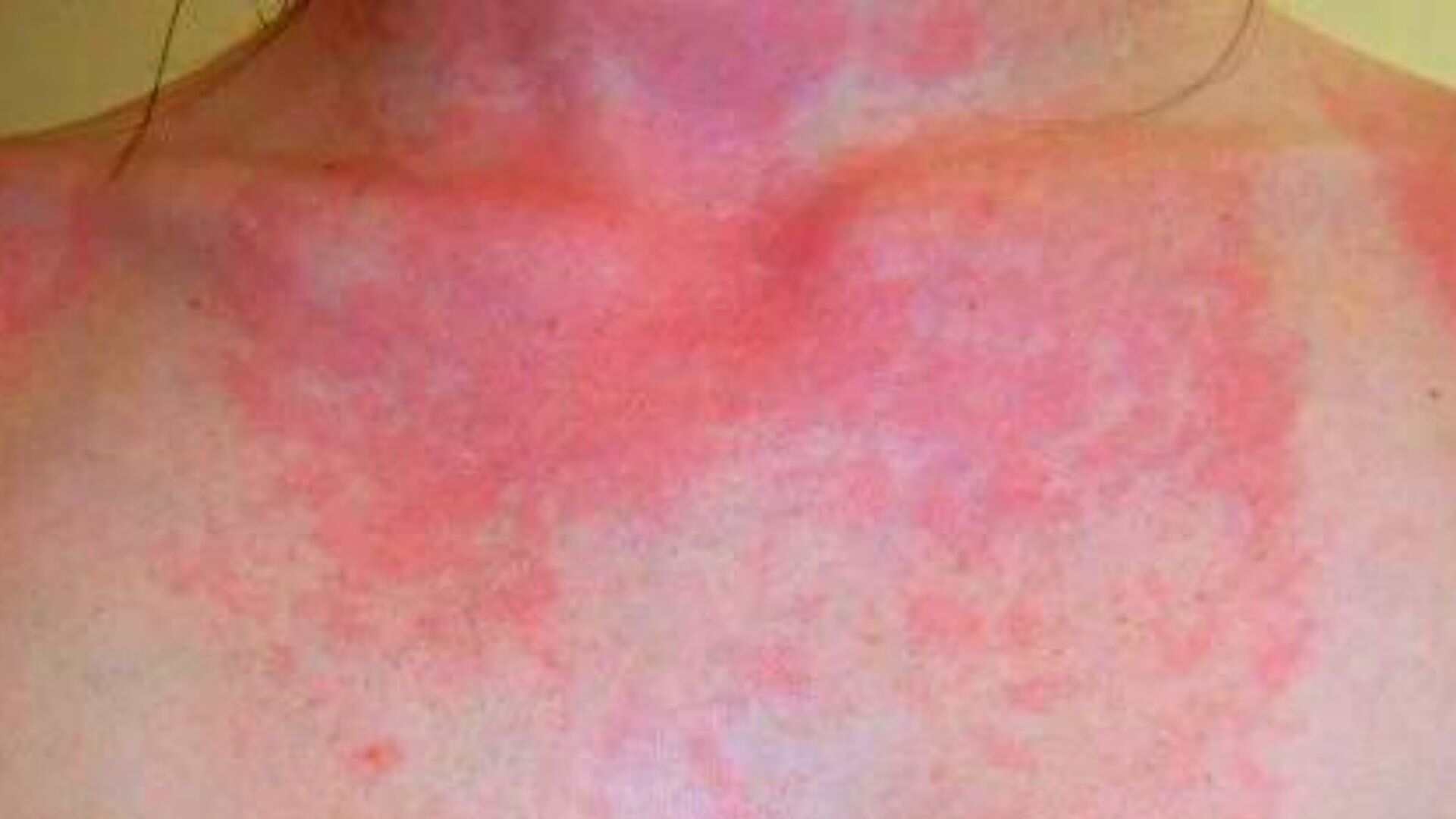
Sun poisoning is a severe reaction to prolonged exposure to the sun's ultraviolet (UV) rays, often mistaken for a severe sunburn. Unlike a typical sunburn, sun poisoning can trigger a range of symptoms that might alarm even the most seasoned sunbather. Understanding what sun poisoning looks like is crucial for timely identification and treatment, preventing further health complications. It’s not just about redness and peeling; sun poisoning can manifest through various physical symptoms, such as intense skin rashes, blistering, and even flu-like symptoms. Recognizing these signs early can help manage the condition effectively and prevent long-term skin damage.
For many, the allure of a sunny day is irresistible, drawing them outdoors to soak up the warmth and light. However, it’s essential to approach sun exposure with caution. Sun poisoning is more than just an inconvenience; it’s a serious health risk that can affect anyone, regardless of their skin type or sun tolerance. By familiarizing yourself with the signs of sun poisoning, you can take proactive steps to protect yourself and enjoy the sun safely.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the specifics of what sun poisoning looks like, explore its causes, symptoms, and treatment options, and provide preventive measures to help you enjoy the sun responsibly. Whether you’re planning a beach vacation or simply spending time outdoors, this information will equip you with the knowledge to recognize and respond to sun poisoning effectively.
Read also:Timeless Hairstyles Of Marilyn Monroe Iconic Looks That Shaped Hollywood
Table of Contents
- What is Sun Poisoning?
- Causes of Sun Poisoning
- What Does Sun Poisoning Look Like?
- Symptoms of Sun Poisoning
- How to Diagnose Sun Poisoning?
- Immediate Treatment Options
- Long-term Treatment Strategies
- Preventive Measures
- How to Protect Your Skin?
- Risk Factors
- Complications of Sun Poisoning
- How to Distinguish from Sunburn?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What is Sun Poisoning?
Sun poisoning, also known as polymorphous light eruption or photodermatitis, is an extreme reaction to the sun's UV rays. Unlike a regular sunburn, it involves more severe symptoms and can lead to systemic reactions. Sun poisoning is often a result of prolonged exposure to the sun without adequate protection, affecting individuals with varying degrees of severity.
The term "sun poisoning" might be misleading, as it is not an actual poisoning but rather a severe sunburn with systemic symptoms. It indicates the body's adverse reaction to UV radiation, which can lead to inflammation and damage to the skin's DNA. Understanding sun poisoning helps in recognizing the symptoms early and taking appropriate measures to mitigate its effects.
- Severe sunburn symptoms
- Potential systemic reactions
- DNA damage due to UV exposure
Causes of Sun Poisoning
Sun poisoning occurs when the skin is overexposed to ultraviolet radiation, primarily from the sun. Several factors can increase the risk of developing sun poisoning:
- Prolonged exposure to the sun without sunscreen
- Being at high altitudes or near reflective surfaces like water or snow
- Having fair skin, which is more susceptible to UV damage
- Taking certain medications that increase photosensitivity
- Genetic predispositions to sun sensitivity
Each of these factors contributes to the skin's inability to protect itself against intense UV radiation, leading to sun poisoning. Understanding these causes is key to preventing the condition through protective measures.
What Does Sun Poisoning Look Like?
Recognizing sun poisoning involves identifying several distinct physical symptoms that differentiate it from a mild sunburn. Here are some key indicators:
- Red, rash-like patches on the skin
- Severe blistering and peeling of the skin
- Swelling and pain in the affected areas
- Headaches, nausea, and dizziness
- Fever and chills indicating a systemic response
Unlike a typical sunburn, sun poisoning can cause widespread discomfort and systemic symptoms. These symptoms often appear within hours of sun exposure and can persist for several days, requiring medical attention if severe.
Read also:Savage X Fenty The Phenomenon Revolutionizing Lingerie Fashion
Symptoms of Sun Poisoning
The symptoms of sun poisoning can vary in intensity but generally include a combination of localized and systemic reactions. The most common symptoms include:
- Severe Skin Redness: Intense redness beyond that of a standard sunburn.
- Rashes and Blisters: Painful, itchy rashes, and fluid-filled blisters can develop.
- Swelling: Affected areas may swell, causing discomfort.
- Systemic Symptoms: Headache, nausea, fever, and chills may occur, resembling flu-like symptoms.
These symptoms can hinder daily activities and, if left untreated, may lead to more severe health issues such as dehydration or skin infections.
How to Diagnose Sun Poisoning?
Diagnosing sun poisoning typically involves a physical examination of the skin and a review of the patient's recent sun exposure history. Healthcare professionals might ask about symptoms such as:
- Duration and intensity of sun exposure
- Previous history of sun sensitivity or allergies
- Current medications that might increase photosensitivity
In some cases, further tests might be conducted to rule out other conditions and confirm sun poisoning. Accurate diagnosis is essential for effective treatment and management.
Immediate Treatment Options
Once sun poisoning is diagnosed, immediate treatment aims to alleviate symptoms and prevent further damage. Key steps include:
- Get out of the sun: Move indoors or to a shaded area to prevent further exposure.
- Hydrate: Drink plenty of fluids to combat dehydration.
- Cool compresses: Apply damp, cool cloths to affected areas to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Over-the-counter medications: Use non-prescription pain relievers like ibuprofen to relieve pain and swelling.
- Topical treatments: Apply aloe vera or hydrocortisone creams to soothe skin irritation.
These measures can provide immediate relief and prevent the condition from worsening. However, if symptoms persist or worsen, seek medical attention promptly.
Long-term Treatment Strategies
For severe cases of sun poisoning, long-term treatment strategies may be necessary. These can include:
- Prescription medications: In some cases, stronger anti-inflammatory or pain-relief medications may be required.
- Skin care regimen: A dermatologist may recommend specific skincare products to aid healing and prevent scarring.
- Monitoring: Regular check-ups to monitor skin health and prevent recurrence.
These strategies help manage symptoms and reduce the risk of long-term skin damage, emphasizing the importance of medical guidance in severe cases.
Preventive Measures
Preventing sun poisoning involves adopting protective measures that minimize UV exposure. Essential steps include:
- Use sunscreen: Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 30, reapplying every two hours or after swimming.
- Wear protective clothing: Opt for long-sleeved shirts, wide-brimmed hats, and sunglasses to shield skin from UV rays.
- Seek shade: Avoid direct sun exposure during peak hours, typically between 10 AM and 4 PM.
- Be mindful of reflective surfaces: Water, sand, and snow can intensify UV exposure, so take extra precautions in these environments.
By following these preventive measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of sun poisoning and enjoy the sun safely.
How to Protect Your Skin?
Protecting your skin from sun damage is crucial for preventing conditions like sun poisoning. Here’s how you can safeguard your skin:
- Apply sunscreen generously: Ensure all exposed skin is covered and reapply regularly.
- Wear a wide-brimmed hat: Protect your face, neck, and ears from direct sun exposure.
- Use UV-blocking sunglasses: Protect your eyes and the sensitive skin around them.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking water helps maintain healthy skin and supports the body's natural defenses against sun damage.
Implementing these protective strategies can help keep your skin healthy and reduce the likelihood of sun-related issues.
Risk Factors
Certain individuals are at a higher risk of developing sun poisoning due to various factors, including:
- Fair skin, light hair, and light-colored eyes
- Family history of skin cancer or sun sensitivity
- Living in high-altitude or equatorial regions
- Regular use of tanning beds
- Taking medications that increase sensitivity to sunlight
Understanding these risk factors can help at-risk individuals take extra precautions to protect themselves against sun poisoning.
Complications of Sun Poisoning
Sun poisoning can lead to several complications if not addressed promptly, including:
- Dehydration: Severe sunburns can cause fluid loss, leading to dehydration.
- Infections: Blistering skin is prone to infections if not properly cared for.
- Long-term skin damage: Repeated sun poisoning incidents can lead to premature aging and increase the risk of skin cancer.
Recognizing these potential complications highlights the importance of addressing sun poisoning symptoms quickly and effectively.
How to Distinguish Sun Poisoning from Sunburn?
While sunburn and sun poisoning share similarities, there are distinct differences:
- Severity: Sun poisoning results in more severe redness, blistering, and pain than a typical sunburn.
- Systemic Symptoms: Unlike a sunburn, sun poisoning can cause systemic symptoms like nausea, fever, and headaches.
- Duration: Sun poisoning symptoms can last longer and require more intensive treatment.
Understanding these differences ensures accurate identification and appropriate treatment of sun poisoning.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the first signs of sun poisoning?
The first signs of sun poisoning typically include severe redness, itching, and blistering of the skin, along with flu-like symptoms such as headache, fever, and nausea.
Can sun poisoning go away on its own?
Mild cases of sun poisoning may resolve on their own with proper self-care and avoiding further sun exposure. However, severe cases require medical attention to prevent complications.
How long does sun poisoning last?
The duration of sun poisoning symptoms can vary, but they typically last a few days to a week. Severe cases may take longer to heal and may require medical treatment.
Are there home remedies for sun poisoning?
Home remedies for sun poisoning include applying cool compresses, using aloe vera for soothing the skin, staying hydrated, and taking over-the-counter pain relievers. However, consult a healthcare provider for severe symptoms.
Can sun poisoning occur on cloudy days?
Yes, sun poisoning can occur on cloudy days. UV rays penetrate clouds, so it's essential to use sun protection even when it's overcast.
Is sun poisoning more common in certain regions?
Sun poisoning can occur anywhere with significant sun exposure, but it's more common in regions with high UV index levels, such as near the equator or at high altitudes.
Conclusion
Sun poisoning is a serious condition that requires awareness and proactive measures to prevent and treat effectively. Recognizing the symptoms and understanding what sun poisoning looks like can help individuals respond appropriately, minimizing health risks and enjoying the sun safely. By prioritizing skin protection and staying informed about sun safety, you can reduce the likelihood of sun poisoning and maintain healthy skin throughout your life.