Hyperpigmentation on the lower level of skin is a common dermatological concern that affects people of various ages and skin types. This condition is characterized by the darkening of the skin due to an increase in melanin production, the pigment responsible for skin color. Although hyperpigmentation can occur on any part of the body, its presence on the lower layers of the skin can be particularly challenging to treat and understand. It is essential to recognize that hyperpigmentation is not merely a cosmetic issue but can also indicate underlying health concerns that require attention.
Delving into the causes of hyperpigmentation on the lower level of skin reveals a myriad of factors, ranging from genetic predisposition to environmental influences. While some individuals may experience this condition due to prolonged sun exposure, others may find that hormonal changes or certain medications contribute to the darkening of their skin. Understanding these causes is crucial for developing effective treatment strategies that target the root of the issue rather than merely addressing surface-level symptoms. Additionally, gaining insight into the physiological processes that lead to hyperpigmentation can aid individuals in preventing its onset.
Fortunately, advancements in dermatology have led to a range of treatments designed to manage hyperpigmentation on the lower level of skin effectively. These treatments vary from topical applications to more invasive procedures and can be tailored to suit individual needs and preferences. However, selecting the appropriate treatment requires careful consideration of factors such as skin type, severity of the condition, and potential side effects. By exploring the available options and consulting with healthcare professionals, individuals can make informed decisions that promote skin health and improve overall quality of life.
Read also:Unique Ideas For Cool Halloween Costumes Stand Out This Halloween
Table of Contents
- Understanding Hyperpigmentation
- What Causes Hyperpigmentation on the Lower Level of Skin?
- How is Hyperpigmentation Diagnosed?
- Effective Treatment Options for Hyperpigmentation
- How to Prevent Hyperpigmentation?
- Lifestyle Adjustments for Healthier Skin
- Does Hyperpigmentation Affect Emotional Well-being?
- Common Misconceptions about Hyperpigmentation
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
Understanding Hyperpigmentation
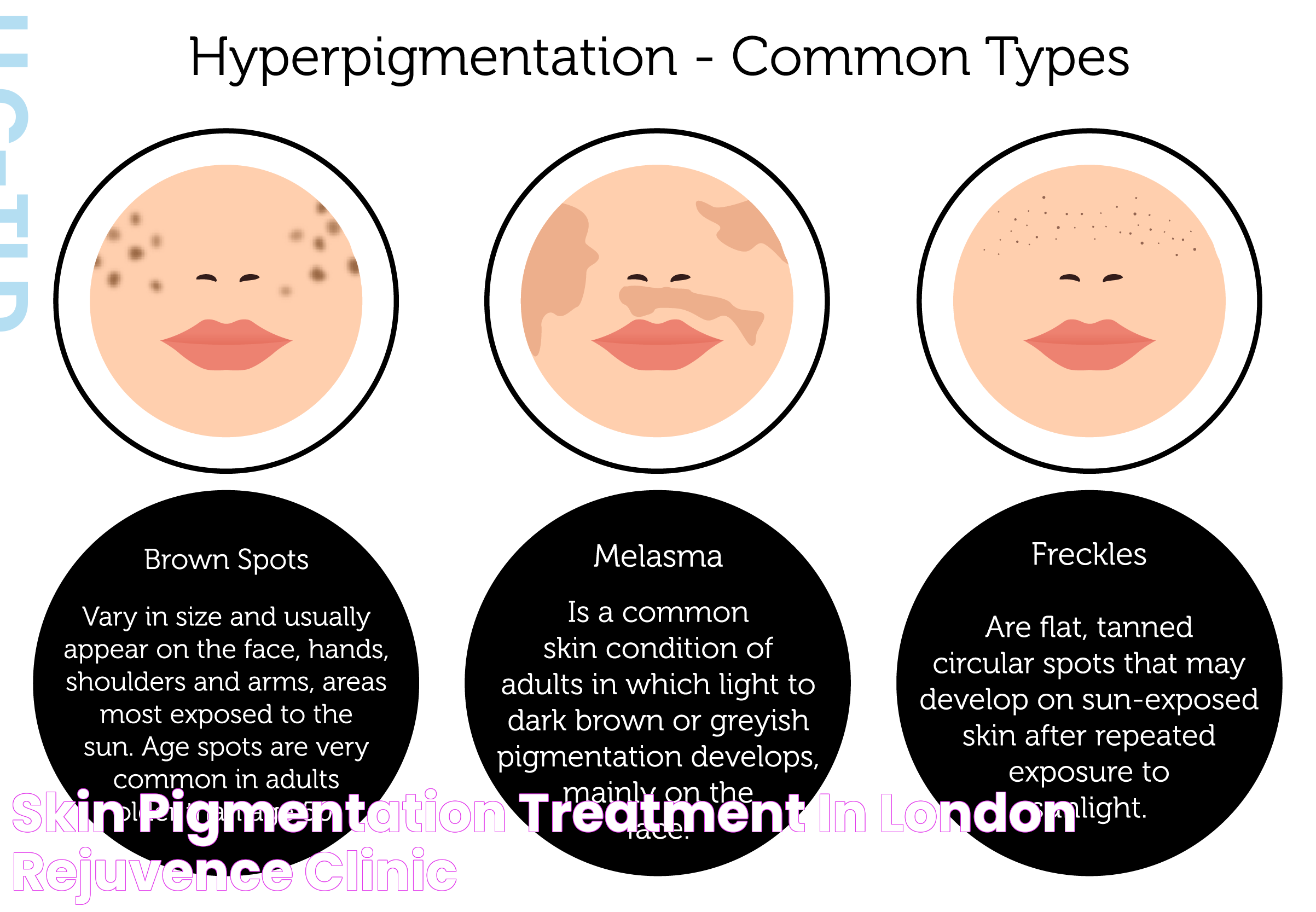
Hyperpigmentation is a condition characterized by the darkening of certain areas of the skin, resulting from an overproduction of melanin. Melanin, the natural pigment responsible for skin color, can become concentrated in patches due to various internal and external factors. This condition can manifest on the skin's surface or deeper layers, each with distinct causes and treatment approaches.
The lower level of the skin, known as the dermis, is where more challenging cases of hyperpigmentation can arise. The dermis houses critical structures like blood vessels, nerves, and hair follicles, making hyperpigmentation in this layer more complex to address. Factors such as inflammation, prolonged sun exposure, and hormonal changes can influence melanin production, leading to pigmentation issues on this deeper skin level.
Understanding the intricacies of hyperpigmentation on the lower skin level is essential for developing targeted treatment strategies. By delving into the underlying causes and mechanisms of this condition, individuals and healthcare professionals can better address the root of the issue, leading to more effective and lasting results.
What Causes Hyperpigmentation on the Lower Level of Skin?
Genetic Factors and Their Role
Genetic predisposition is a significant factor in the development of hyperpigmentation on the lower level of skin. Certain individuals may inherit a tendency to produce more melanin, putting them at a higher risk of developing pigmentation issues. This genetic component can influence how the skin responds to various triggers, such as sun exposure or hormonal changes.
Research indicates that specific genes are involved in the regulation of melanin production and distribution. Variations in these genes can lead to differences in skin tone and susceptibility to hyperpigmentation. Understanding one's genetic makeup can provide valuable insights into the potential risk of developing this condition and guide preventive measures and treatment decisions.
Environmental Influences
Environmental factors play a crucial role in the onset of hyperpigmentation on the lower level of skin. Sun exposure is one of the most common triggers, as ultraviolet (UV) rays stimulate melanin production as a protective response. Over time, excessive sun exposure can lead to the accumulation of melanin in specific areas, resulting in dark patches.
Read also:Why Do My Nails Have Dents Causes And Solutions
Pollution and exposure to certain chemicals can also contribute to hyperpigmentation. These environmental aggressors can induce inflammation and oxidative stress in the skin, disrupting normal melanin production and distribution. Implementing protective measures such as using sunscreen and avoiding prolonged exposure to pollutants can help mitigate these environmental impacts.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations, particularly during pregnancy, menopause, or as a side effect of certain medications, can influence melanin production and lead to hyperpigmentation. Conditions such as melasma, commonly referred to as the "mask of pregnancy," are directly linked to hormonal changes and can result in dark patches on the skin, including the lower layers.
Understanding the hormonal influences on skin pigmentation is important for individuals experiencing hyperpigmentation related to these changes. Hormonal therapies or adjustments in medication may be necessary to address the root cause of the condition and prevent further pigmentation issues.
How is Hyperpigmentation Diagnosed?
Recognizing Symptoms
Hyperpigmentation symptoms can vary depending on the underlying cause and the depth of the affected skin layers. Common indicators include dark patches or spots, uneven skin tone, and areas of discoloration. These symptoms may appear on the face, hands, or other sun-exposed areas, but can also occur on the lower levels of the skin, leading to more persistent cases.
In some instances, hyperpigmentation may be accompanied by other skin conditions such as inflammation or irritation. Identifying the specific symptoms and their severity is crucial for determining the appropriate course of treatment and addressing any underlying health concerns.
Diagnostic Tools and Techniques
Diagnosis of hyperpigmentation typically involves a thorough examination of the skin by a dermatologist. This process may include a visual assessment, a review of the patient's medical history, and inquiries into potential triggers such as sun exposure, hormonal changes, or medication use.
In some cases, additional diagnostic tools and techniques may be employed to assess the depth and severity of the pigmentation. These may include dermoscopy, which allows for a closer examination of the skin's surface, or a biopsy, where a small skin sample is taken for further analysis. These diagnostic approaches can provide valuable insights into the nature of the hyperpigmentation and guide treatment decisions.
Effective Treatment Options for Hyperpigmentation
Topical Applications
Topical treatments are often the first line of defense against hyperpigmentation on the lower level of skin. These products typically contain active ingredients such as hydroquinone, retinoids, or vitamin C, which work to lighten dark patches and even out skin tone. Consistent and correct application of these treatments is essential for achieving optimal results.
In addition to over-the-counter options, prescription-strength topical treatments may be recommended for more severe cases. Consulting with a dermatologist can help determine the most suitable product based on the individual's skin type and the severity of the pigmentation.
Laser Therapy
Laser therapy is a more advanced treatment option for hyperpigmentation, particularly effective for addressing pigmentation issues on deeper skin layers. This approach involves the use of targeted laser beams to break down excess melanin and stimulate collagen production, promoting skin regeneration and a more even complexion.
Different types of laser treatments are available, each with varying levels of intensity and effectiveness. It is crucial to discuss the potential benefits and risks with a qualified healthcare professional to ensure that laser therapy is the appropriate choice for the individual's needs.
Chemical Peels
Chemical peels are another treatment option for hyperpigmentation, involving the application of a chemical solution to exfoliate the skin and remove the outermost layer. This process encourages the growth of new, more evenly pigmented skin and can be particularly beneficial for addressing pigmentation on the lower levels of the skin.
The intensity of a chemical peel can vary, with lighter peels targeting surface-level pigmentation and deeper peels addressing more severe cases. As with other treatment options, consulting with a dermatologist is essential to determine the most appropriate approach based on the individual's skin type and condition.
How to Prevent Hyperpigmentation?
Preventing hyperpigmentation on the lower level of skin involves a proactive approach to skincare and lifestyle choices. Implementing protective measures can help mitigate the risk of developing pigmentation issues and promote overall skin health.
Key prevention strategies include:
- Applying broad-spectrum sunscreen daily to protect against UV rays.
- Wearing protective clothing, such as hats and long sleeves, when outdoors.
- Using skincare products that contain antioxidants and anti-inflammatory ingredients.
- Avoiding prolonged exposure to environmental pollutants and irritants.
- Maintaining a consistent skincare routine tailored to individual skin needs.
Lifestyle Adjustments for Healthier Skin
Dietary Influences
Diet plays a crucial role in maintaining skin health and preventing hyperpigmentation. Consuming a balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants can support skin regeneration and protect against oxidative stress, a contributing factor to pigmentation issues.
Key dietary recommendations include:
- Incorporating a variety of fruits and vegetables, particularly those high in vitamin C and E.
- Ensuring adequate hydration to maintain skin moisture and elasticity.
- Limiting the intake of processed foods and sugars, which can contribute to inflammation.
- Including omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish and nuts, to support skin barrier function.
Protecting Against Sun Exposure
Sun exposure is a major trigger for hyperpigmentation, making sun protection a critical aspect of prevention. In addition to wearing sunscreen, taking additional protective measures can significantly reduce the risk of developing pigmentation issues.
Recommendations for sun protection include:
- Seeking shade during peak sun hours (10 AM to 4 PM).
- Wearing wide-brimmed hats and UV-blocking sunglasses.
- Opting for clothing with built-in sun protection.
- Regularly reapplying sunscreen, especially after swimming or sweating.
Does Hyperpigmentation Affect Emotional Well-being?
Hyperpigmentation can have a significant impact on an individual's emotional well-being and self-esteem. The visible nature of the condition can lead to feelings of self-consciousness and social anxiety, particularly if the pigmentation is prominent or affects noticeable areas.
Addressing the emotional impact of hyperpigmentation is important for improving overall quality of life. Seeking support from mental health professionals or joining support groups can provide a valuable outlet for individuals coping with the psychological effects of this condition. Additionally, pursuing effective treatment options can help boost confidence and improve self-image.
Common Misconceptions about Hyperpigmentation
There are several misconceptions surrounding hyperpigmentation, which can lead to confusion and ineffective treatment approaches. Understanding the truths about this condition is crucial for developing effective management strategies.
Common misconceptions include:
- Hyperpigmentation is solely a cosmetic issue: While it affects appearance, it can also indicate underlying health concerns.
- All hyperpigmentation is the same: Different types require distinct treatment approaches.
- Home remedies are always effective: Professional guidance is often necessary for severe cases.
- Hyperpigmentation will resolve on its own: Without intervention, it may persist or worsen over time.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can hyperpigmentation be completely cured? Hyperpigmentation can often be managed effectively, but complete cure depends on the underlying cause and individual response to treatment.
2. Are natural remedies effective for hyperpigmentation? Some natural remedies may offer mild benefits, but professional treatments are usually more effective for significant pigmentation issues.
3. How long does it take to see results from treatment? The time frame varies based on the treatment method and individual skin response, but noticeable improvements may take several weeks to months.
4. Is hyperpigmentation more common in certain skin types? Yes, individuals with darker skin tones may be more prone to hyperpigmentation due to higher melanin levels.
5. Can stress contribute to hyperpigmentation? Stress can exacerbate skin conditions, potentially worsening hyperpigmentation through hormonal and inflammatory pathways.
6. Are there any side effects of hyperpigmentation treatments? Side effects vary depending on the treatment, but can include skin irritation, redness, or increased sensitivity. Consulting with a dermatologist is essential to minimize risks.
Conclusion
Hyperpigmentation on the lower level of skin is a multifaceted condition that requires a comprehensive understanding of its causes, diagnosis, and treatment options. By recognizing the genetic, environmental, and hormonal influences on skin pigmentation, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent and manage this condition. With advancements in dermatological treatments, effective solutions are available to address hyperpigmentation, improve skin health, and enhance emotional well-being. Consulting with healthcare professionals, adopting preventive measures, and making informed lifestyle choices are key strategies for achieving and maintaining healthy, even-toned skin.